- +91 91360 95925
- hello@auroskin.in
- 2nd Floor, Sapphire Plaza, Opp CNM School, Dadabhai Road, Vile Parle West, Mumbai
- About Us
- Services
- SKIN
- HAIR
- NAIL
- DIAGNOSTICS
- DERMATOSURGERY
- LASER TREATMENTS
- AESTHETICS
- RF Skin Tightening Treatment
- Profilo Treatment
- Micropigmentation Treatment
- Dark Circle Removal Treatment
- Laser Vaginal Tightening Treatment
- Open Pores Treatment
- Botox Treatment
- Thread Lift Treatment
- Fillers Treatment
- Skin Patch Testing | Allergy Testing Service
- Fillers Treatment
- Double Chin Reduction Treatment
- Patient Reviews
- FAQ’s
- Gallery
- Blogs
- Appointments
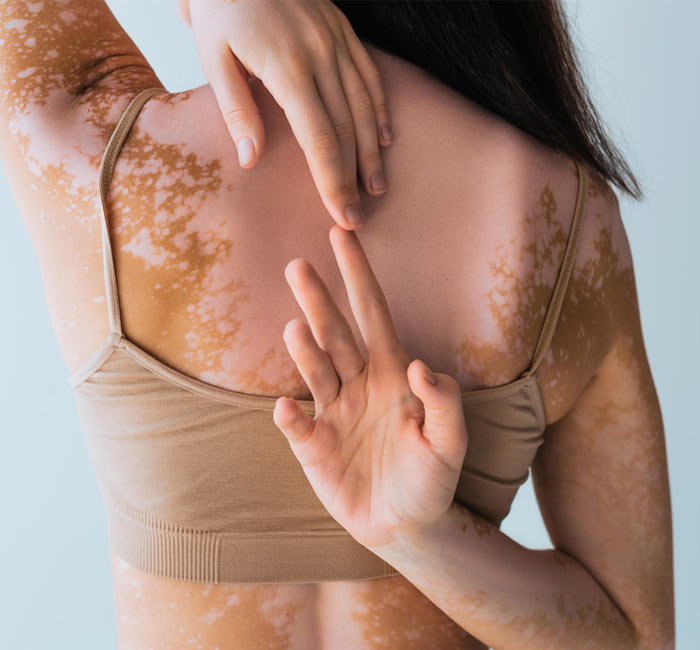
If you’re struggling with white patches on your skin, you’re not alone. Vitiligo can affect your confidence, but effective treatments are available to restore your skin’s natural tone. At Auro Skin Clinic, we specialise in laser vitiligo treatment in Mumbai, using the latest laser technology to target and re-pigment the affected areas. Our advanced techniques offer a safe, non-invasive solution for white spot treatment in Mumbai, helping you get back a smoother, even skin tone with long-lasting results.
What is Laser Vitiligo Treatment?
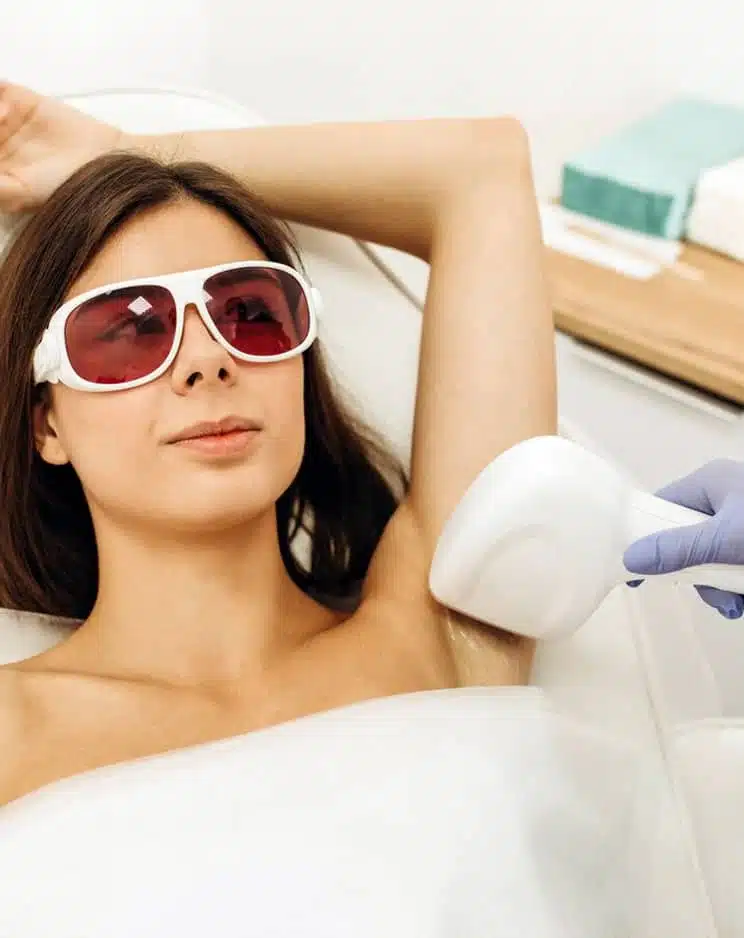
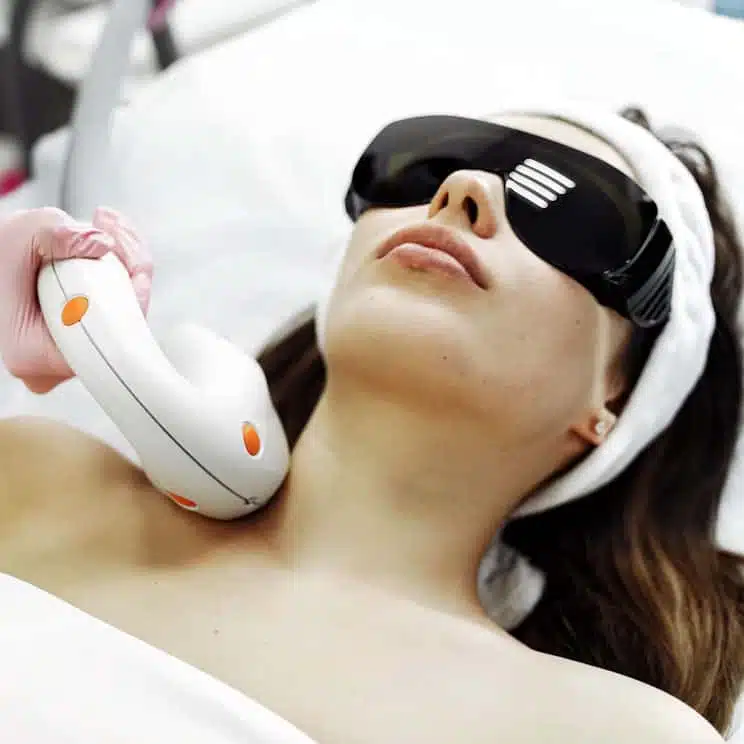
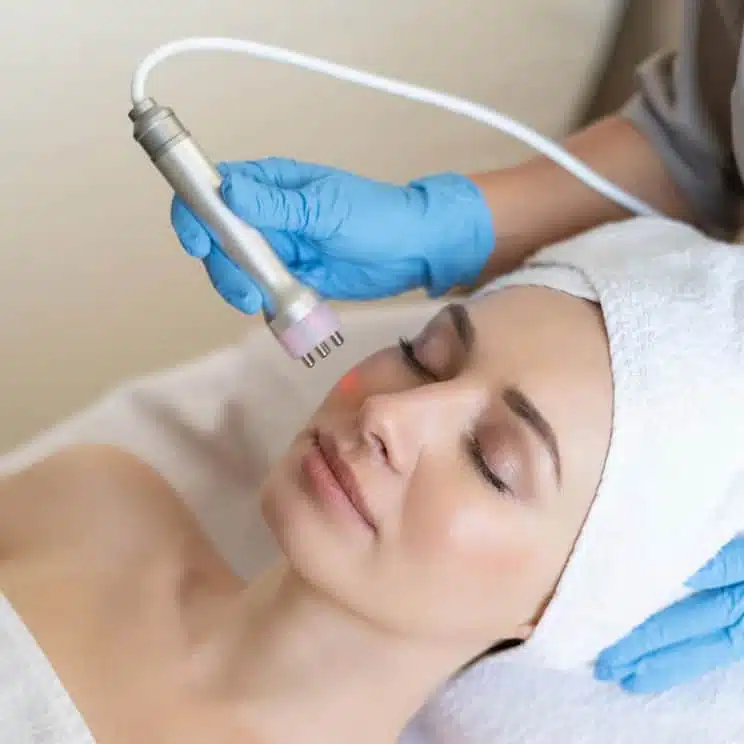
Laser vitiligo treatment is a non-invasive procedure that helps stimulate melanocyte activity in the affected areas of the skin. The treatment involves the use of targeted laser light to encourage pigment production and restore skin colour in areas where it has been lost due to vitiligo. The laser penetrates the skin’s deeper layers, promoting healing and repigmentation. This is highly effective for people with localised patches and is a safe and efficient alternative to other treatments. At Auro Skin Clinic, we offer laser vitiligo treatment in Vile Parle to help you get natural-looking skin tone restoration.
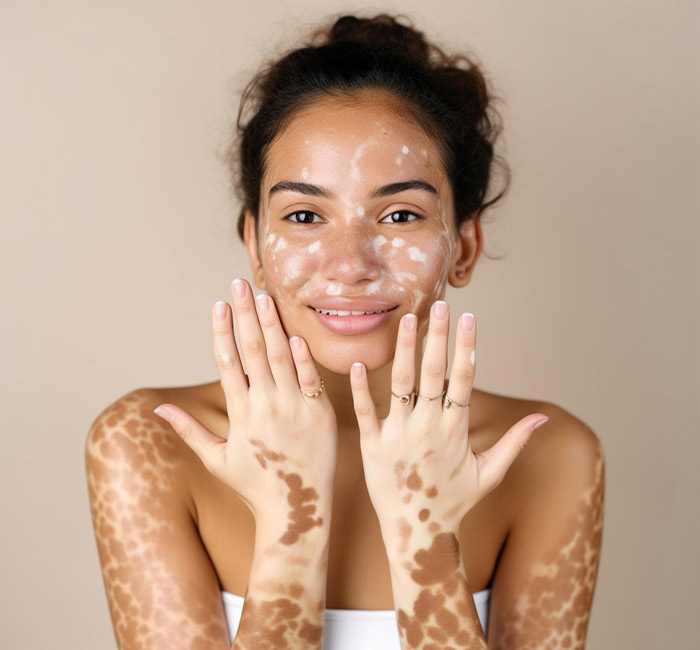
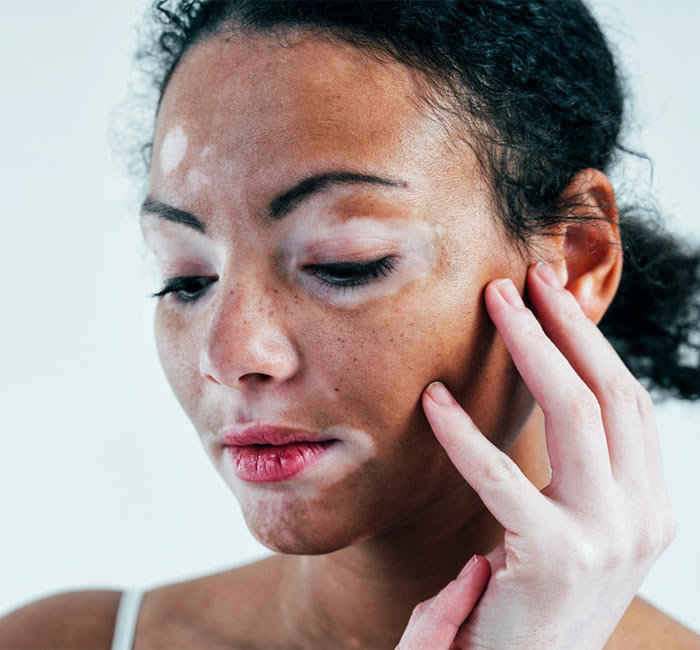


Laser Vitiligo Treatment Procedure
1. Consultation
The first step is a consultation with our expert dermatologist in Mumbai. During the consultation, our specialists will examine the affected areas to assess the severity of vitiligo. We will also consider your medical history and discuss any previous treatments. Based on the assessment, we will customise a treatment plan based on your individual needs and skin type.2. Pre-Procedure Care
Before the treatment, we advise our patients to follow some guidelines to optimise the procedure results. Sometimes, patients may be advised to use topical treatments to prepare the skin for the laser session.3. Procedure
During the treatment, our specialists will use a specialised Eximal laser that emits controlled pulses of light, which will be applied directly to the white patches of skin. The laser will stimulate the melanocytes in the affected areas to produce melanin and restore pigmentation. Depending on the size of the patches, multiple sessions may be required to achieve optimal results.4. Aftercare
Post-treatment care is crucial to get the best results. Patients are advised to avoid direct sun exposure and use sunscreen on the treated skin. Our specialists will provide a personalised aftercare plan and instructions for follow-up treatments to monitor progress and adjust as needed.Laser Treatments
Benefits of Laser Vitiligo Treatment
- Restores Skin Pigmentation: Auro Skin Clinic offers Laser treatment in Mumbai that helps stimulate the melanocytes in the skin to produce melanin, helping to restore the skin's natural colour.
- Non-Invasive Procedure: In contrast to surgical options, laser vitiligo treatment is not invasive, and no incisions or cuts are made.
- Little Downtime: Most patients have minimal to zero downtime after the procedure, and they can resume their usual activities.
- Targeted Treatment: Laser technology enables the precise treatment of white spots on the skin, providing a better solution for localised vitiligo.
- Safe And Effective: Laser treatment for vitiligo is a safe and established method to restore skin pigmentation with fewer side effects.
- Boosts Confidence: Restoration of the natural skin colour can profoundly impact an individual's self-confidence and self-esteem, minimising the emotional effect of vitiligo.
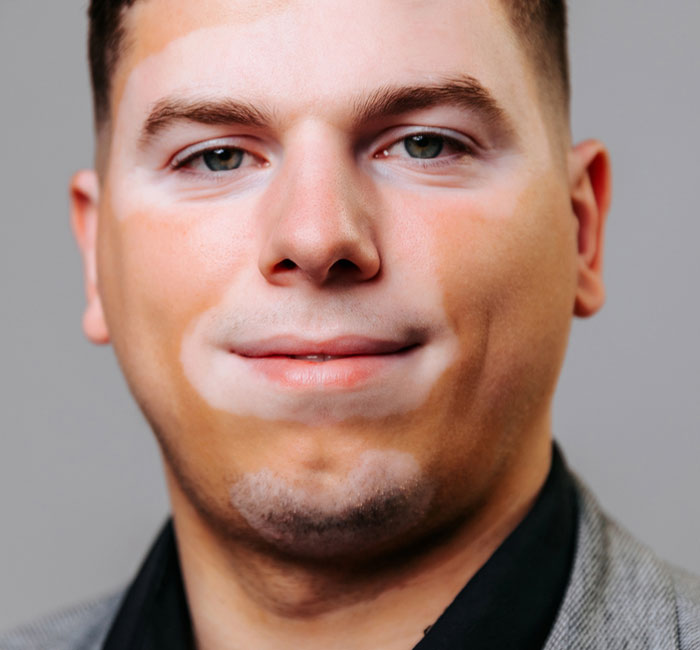

Why Choose Auro Skin Clinic?
At Auro Skin Clinic, we are experts at offering efficient laser vitiligo treatment in Vile Parle, focusing on individualised care for each patient. Our experienced dermatologists specialise in the current laser technology and ensure that your treatment is completely safe and highly effective.
Your comfort and well-being are our priorities. We offer patient-focused solutions for treating white spots on the skin, utilising cutting-edge technology to achieve the best long-term results. For an effective solution for vitiligo, schedule a consultation at Auro Skin Clinic today and explore our innovative laser vitiligo treatment for safe, noticeable results.
FAQs For Laser Vitiligo Treatment in Mumbai
1. Is laser treatment effective for every form of vitiligo?
It's extremely effective on localised vitiligo, especially for smaller patches. However, the outcome can vary based on the severity and extent of the condition. Bigger areas or more severe cases may require additional treatments.
2. How does laser treatment work for vitiligo?
Laser treatment functions by sending pulses of light that stimulate melanocytes to create melanin. This stimulates the repigmentation of those white areas, restoring your skin's natural colour over time.
3. Is laser treatment a permanent cure for vitiligo?
Although laser treatment can help by restoring pigmentation, it is not a permanent cure. Ongoing treatment and maintenance could be required to maintain the results and avoid further skin depigmentation.
4. How much is laser vitiligo treatment?
The price depends on the treatment area and the number of sessions needed. At Auro Skin Clinic, we provide affordable treatment packages for your needs. Get in touch with us for a consultation and customised cost information
Get Support