- +91 91360 95925
- hello@auroskin.in
- 2nd Floor, Sapphire Plaza, Opp CNM School, Dadabhai Road, Vile Parle West, Mumbai
- About Us
- Services
- Skin
- Hair
- Nail
- Diagnostics
- Dermatosurgery
- Laser Treatments
- Aesthetics
- RF Skin Tightening Treatment
- Profilo Treatment
- Micropigmentation Treatment
- Dark Circle Removal Treatment
- Laser Vaginal Tightening Treatment
- Open Pores Treatment
- Botox Treatment
- Fillers Treatment
- Thread Lift Treatment
- Skin Patch | Allergy Testing Service
- Fillers Treatment
- Exosome Treatment
- Double Chin Reduction Treatment
- Patient Reviews
- Gallery
- Blogs
- Appointments
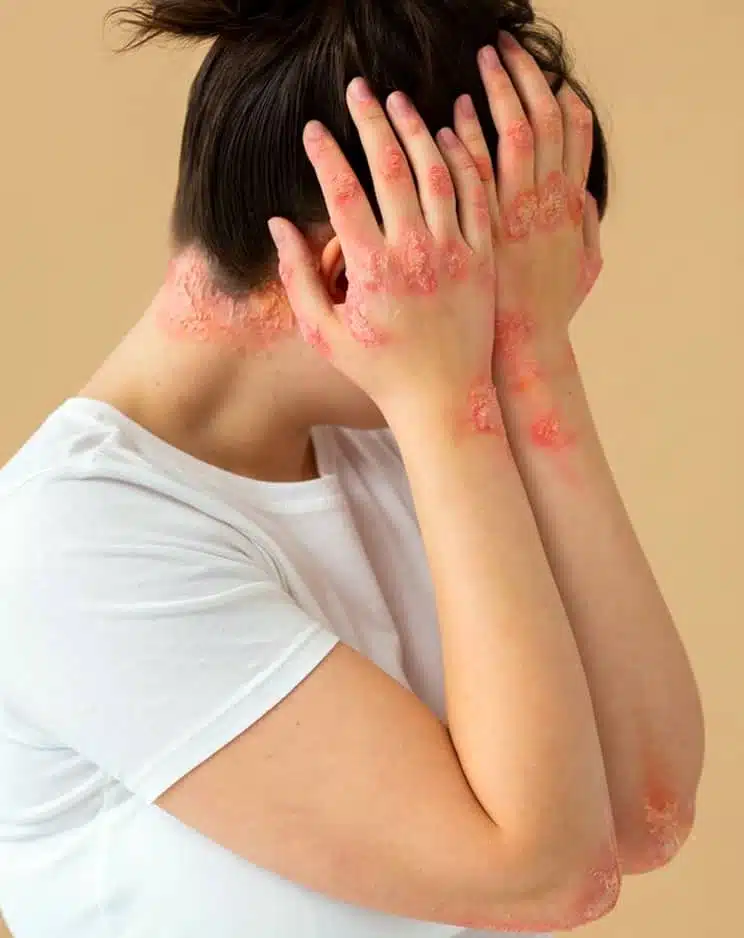
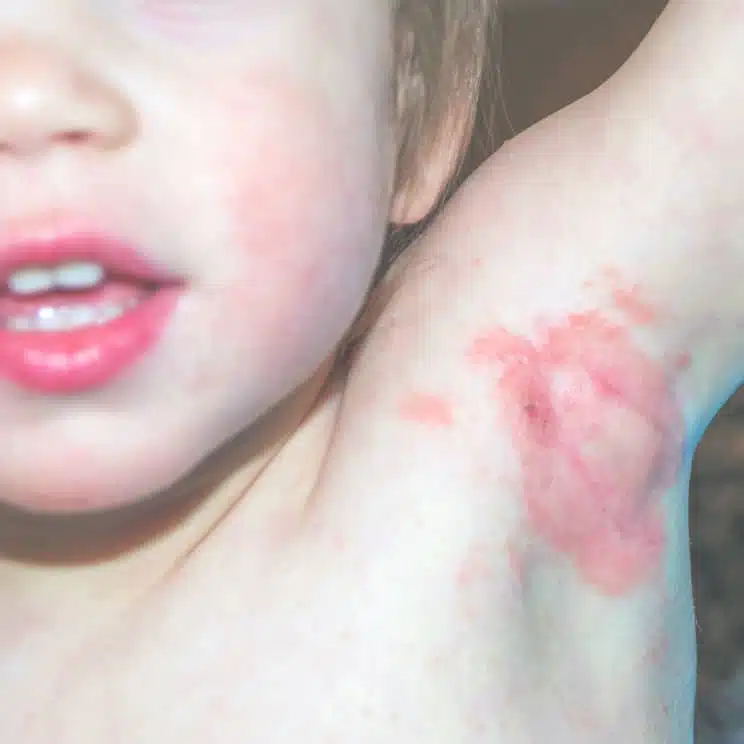
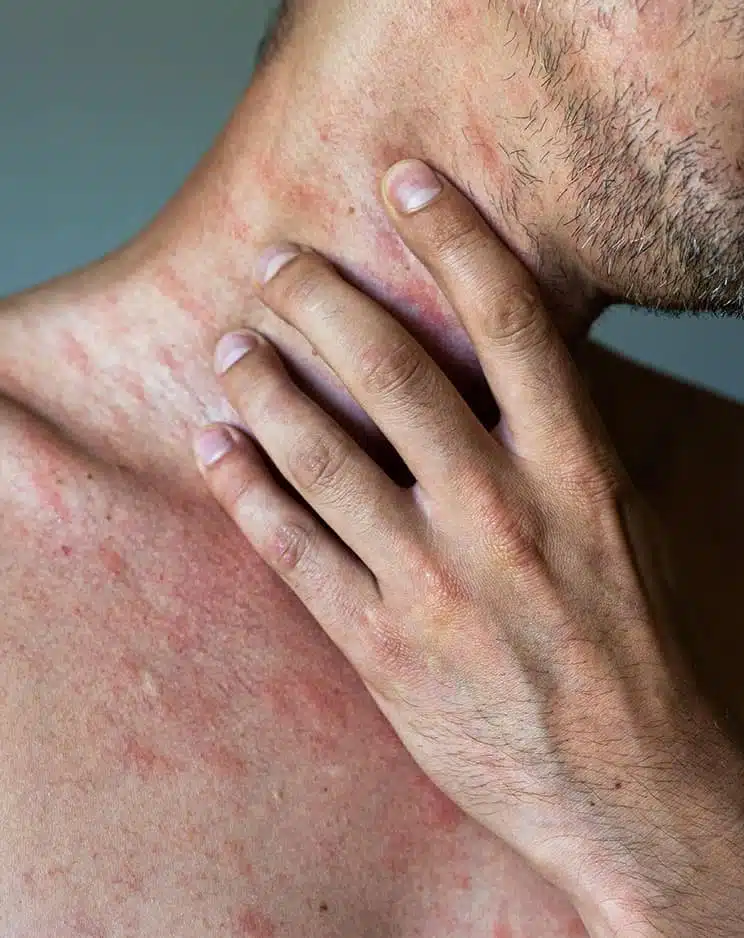
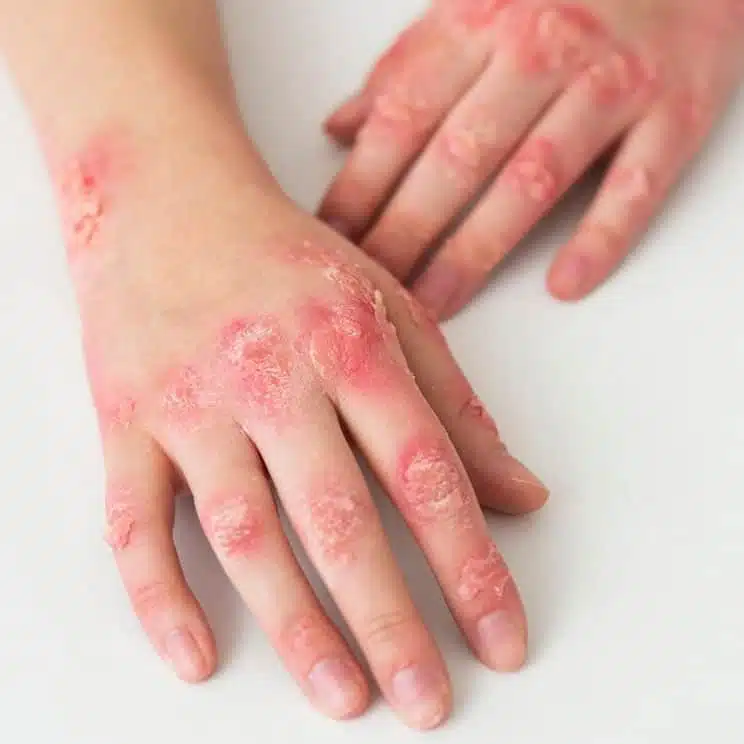
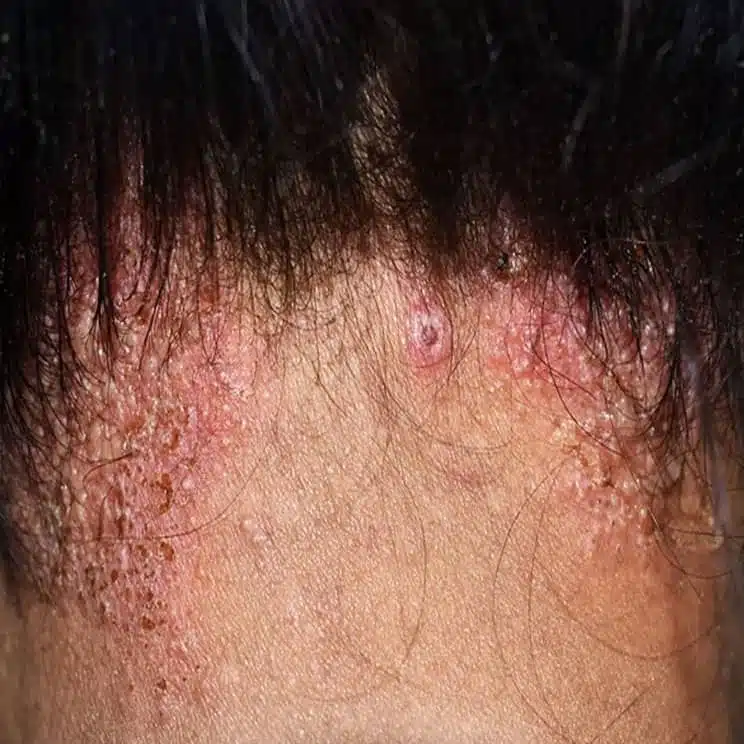
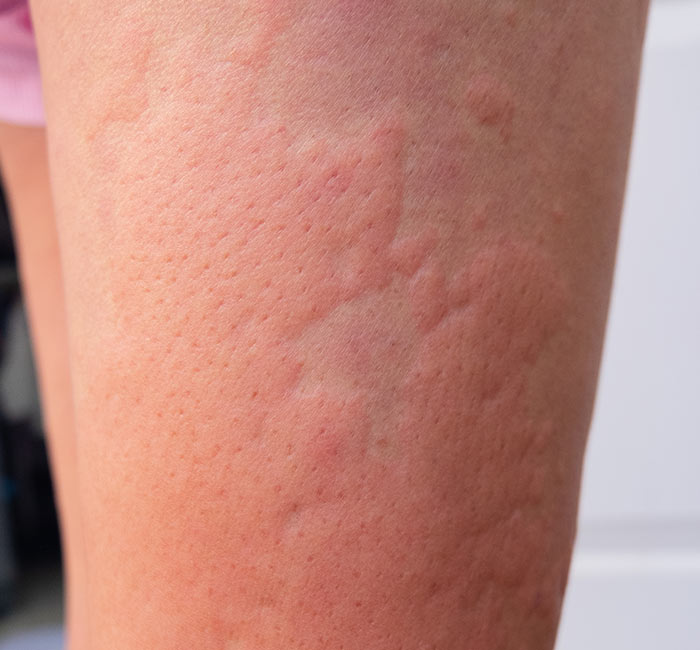
Do you have sudden red, itchy welts that show up out of nowhere, only to vanish just as unexpectedly? You may be dealing with urticaria, or hives. While it may seem like a harmless irritation, these flare-ups can be uncomfortable and might make you self-conscious. At Auro Skin Clinic, we provide urticaria treatment in Vile Parle, Mumbai, that is tailored to your requirements and helps you manage the condition.
What is Urticaria (Hives)?
Urticaria, or hives, refers to a skin condition characterised by raised, itching, and red hives that can occur anywhere on the body. These hives can last from a few hours to a few days and usually come suddenly. The condition is generally caused by allergens, stress, changes in temperature, or even unidentified causes.
If you’re searching for treatment for hives in Mumbai, understanding the root cause of your symptoms is the first step toward relief. At Auro Skin Clinic, our goal is not just to manage the symptoms but to uncover what’s causing the problem in the first place.
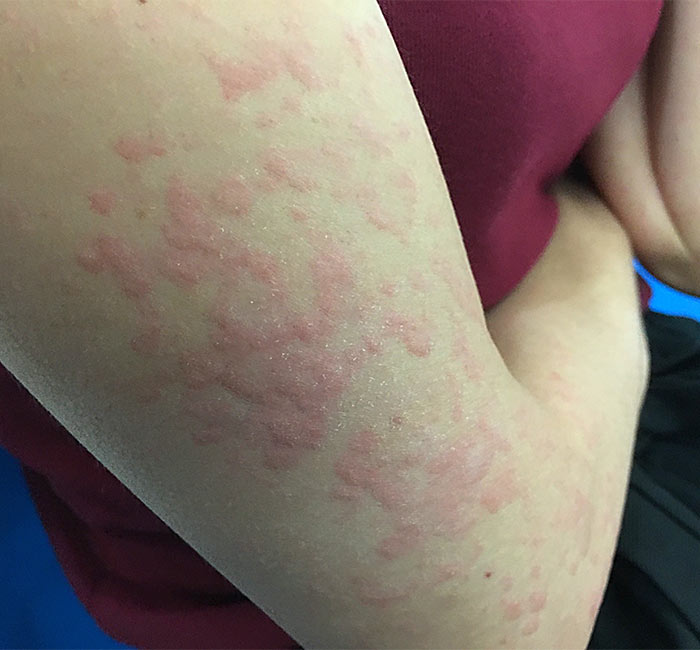
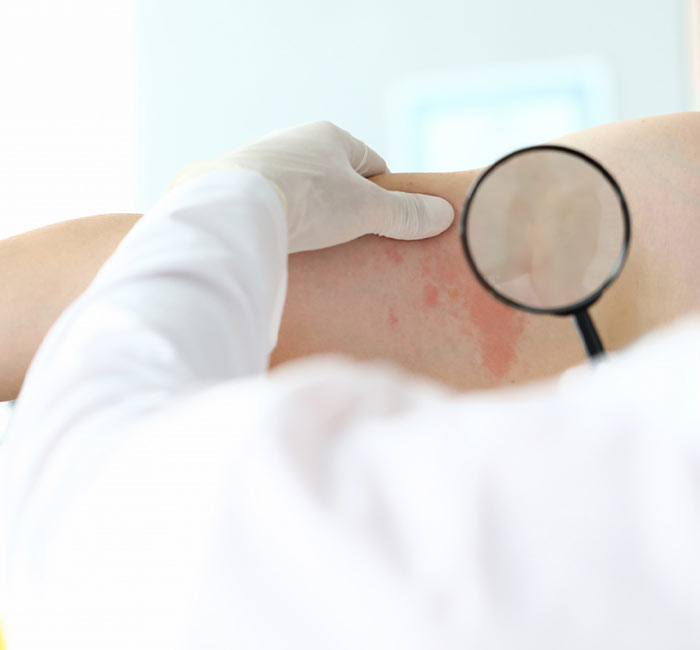
Urticaria Treatment Procedure
When you visit us, our dermatologists in Vile Parle will conduct a detailed skin assessment and medical history to understand your symptoms, triggers, and flare-ups. After the consultation, our experts will create a tailored treatment plan which involves medication like:
- Antihistamines to minimise allergic reactions
- Short-term corticosteroids for severe outbreaks
- Immunosuppressive drugs (if chronic)
- Lifestyle and dietary changes
- Allergy elimination and testing strategies
We make every effort to offer long-lasting relief through combinations of skin treatments and preventive care, making us a trusted destination for hives treatment in Vile Parle and across Mumbai.
Benefits of Urticaria Treatment
Getting skin treatment in Mumbai for urticaria on time has many advantages:
- Less Itching and Discomfort: Proper medication reduces the severity and frequency of symptoms.
- Prevention of Recurrences: We identify and manage your triggers, so fewer flare-ups over time.
- Personalised Treatment Plans: Each treatment is customised to your condition, so the medication and strategies used are best for your symptoms.
- Long-Term Skin Health: Our holistic approach improves overall skin health, so you are less prone to future outbreaks and your skin is balanced.
- Confidence Boost: Our treatment helps you get your confidence back by reducing the discomfort and visible effects of hives, so you can feel comfortable in your skin again.
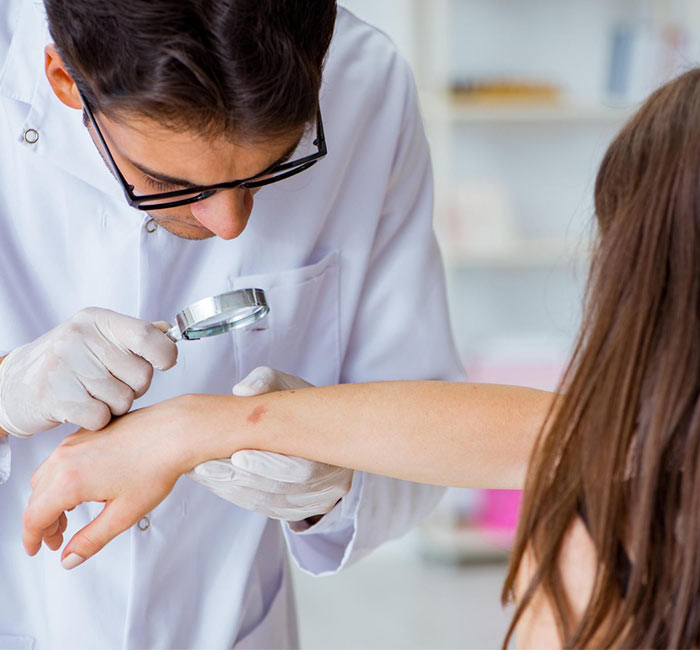
Why Choose Auro Skin Clinic For Urticaria Treatment in Mumbai
At Auro Skin Clinic, we offer expert treatment for urticaria in Vile Parle, Mumbai, using advanced treatment methods to target the root of your symptoms. Our dermatologists provide customised solutions for your specific needs so that you can get the best treatment for immediate relief and long-term management. We focus on not just relieving the discomfort but also improving your overall skin health and preventing future flare-ups. With a holistic approach to treatment and your well-being in mind, Auro Skin Clinic is your partner in managing urticaria
Ready to take control of your skin and say goodbye to hives? Book your appointment today with our experts and start your journey to lasting relief.
FAQs For Urticaria Treatment in Mumbai
1. What is the best treatment for urticaria?
The most common treatment for urticaria involves Antihistamines for allergic reactions and identifying and avoiding triggers. For chronic cases, the dermatologist may recommend immunosuppressants or biologic therapies.
2. What is the cause of urticaria?
The causes of urticaria include allergens (food, medications), infections, autoimmune, stress, or temperature changes. In many cases, the cause is unknown; that’s why a professional consultation with a dermatologist is necessary.
3. How to cure urticaria permanently?
While not all cases of urticaria have a permanent cure, long-term management through medication, trigger avoidance, and lifestyle changes can reduce or eliminate flare-ups.
4. How to get rid of hives?
At the first sign of a breakout, apply a cold compress and take prescribed antihistamines to eliminate hives. If the hives continue or worsen, see a dermatologist to determine the next steps.
Get Support